

The easiest way to find the pattern of a sequence is to first see whether each number is divisible by the previous one. We can’t classify the third one, as the numbers are all equal to each other. The second sequence is weakly increasing, because each number is greater than or equal to the one before it. The first sequence is strictly decreasing because each number is less than the one before it.

Give an explanation to justify your answer. Weakly monotonicĬlassify the following sequences as either weakly monotonic or strictly monotonic, as well as whether it is increasing or decreasing.

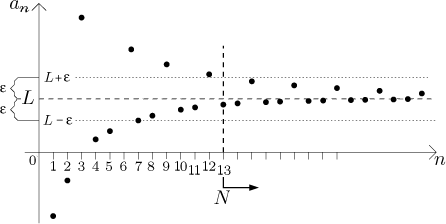
In other words, as the limit of the sequence increases towards infinity, it converges, or meets, some number. Sequence $a_$ is decreasing and bounded below In order for the theorem to work, we have to have three conditions, found in the table below. The monotone convergence theorem deals with monotonic sequences. Weakly monotonicĮach number is less than or equal to the one that came before itĮach number is less than the one that came before itĪn example of a weakly decreasing monotonic sequence can be seen below.Īn example of a strictly decreasing monotonic sequence can be seen below. One thing they have in common is that decreasing monotonic sequences can also be weakly or strictly decreasing. Decreasing Monotonic SequenceĪ decreasing monotonic sequence is the exact opposite of an increasing monotonic sequence. This sequence, in comparison, is strictly increasing as each number is greater than the last. Each number is equal to or greater than the previous one.Let’s look at an example of each of the above types of increasing monotonic sequences.Īs you can see, this is a weakly monotone increasing sequence because it is: There are two types of increasing monotonic sequences:Įach number is greater than or equal to the one that came before itĮach number is greater than the one that came before it When a monotonic sequence is increasing, each number is greater than the one that came before it. Increasing Monotonic SequenceĪ monotonic sequence can be either increasing or decreasing. Ī sequence is defined as a collection of objects, usually numbers, where order matters and where a pattern can be, but is not always, exhibited.Ī monotone sequence is a special kind of sequence, where the number before it is either greater or less than the one before it. Possible inequalities and their descriptions can be found in the table below. Inequalities are operations that compare two or more numbers. We can easily plot inequalities on a number line. A number line holds all real numbers, an example can be seen in the image below. Let's go Monotone Sequence Definition In order to understand what a monotone sequence is, you should be very comfortable with the concept of a number line as well as inequalities.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
